9 Costly Fiber Optic Installation Mistakes and How to Prevent Them
Fiber optic technology is essential for modern communication, offering unparalleled speed, reliability, and efficiency. However, improper installation can lead to severe performance issues, expensive repairs, and unnecessary downtime. To ensure a high-functioning fiber optic network, avoid these nine common fiber optic installation mistakes.
1. Selecting the Wrong Connector Type
The Mistake: Not all fiber optic connectors are the same. SC, LC, ST, and other connector types serve different purposes and aren’t interchangeable. Choosing the wrong connector can cause inefficient signal transmission, high loss rates, or total connection failure.
The Solution: Determine the correct connector type based on your network’s design before installation. Ensure all cables, patch panels, and transceivers are compatible to avoid performance disruptions.
2. Mishandling Fiber Cables
The Mistake: Fiber optic cables contain delicate glass cores easily damaged by bending, kinking, or excessive force. Mishandling during installation can cause micro-cracks, resulting in signal degradation or total failure.
The Solution: Follow the manufacturer’s bend radius recommendations and avoid pulling cables with excessive force. Use proper cable supports and management systems to prevent strain.
3. Poor Cable Termination Practices
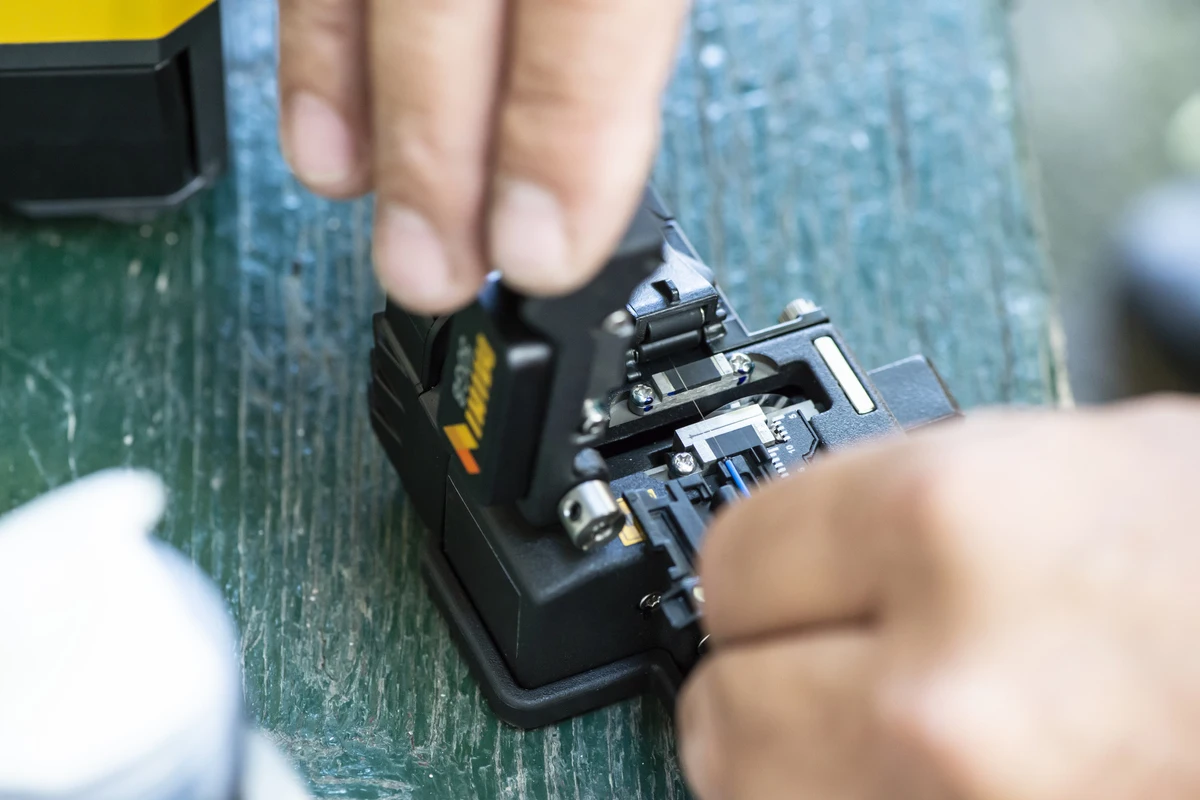
The Mistake: Even a small amount of dirt, dust, or oil from fingerprints can obstruct light transmission, leading to signal loss. Improperly cleaned or incorrectly terminated fiber cables significantly impact network performance.
The Solution: Always clean fiber ends using lint-free wipes and isopropyl alcohol before termination. Use high-quality termination tools and test each connection to verify optimal performance.
4. Skipping Comprehensive Testing
The Mistake: Some installers assume that fiber optic cables are flawless out of the box and fail to conduct thorough testing. This often leads to undetected defects, which can cause major troubleshooting challenges later.
The Solution: Every fiber optic cable should undergo proper testing, including:
- Optical Power Testing to measure signal loss.
- Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) Testing to detect faults, bends, or breaks.
- Continuity Testing to confirm proper light transmission.
Testing at multiple stages of the installation process ensures long-term network reliability.
5. Incorrect Cable Length Estimation
The Mistake: Ordering fiber optic cables that are too long or too short can lead to wasted materials, increased costs, and inefficient routing. Excess cable can cause clutter, while insufficient cable may require additional splicing.
The Solution: Carefully measure cable routes before ordering. Allow some slack to accommodate unexpected bends and reroutes, but avoid excessive excess that leads to messy installations.
6. Exceeding Maximum Cable Distance
The Mistake: Fiber optic cables have distance limitations depending on the type (single-mode or multimode). Exceeding these distances can weaken signals, increase latency, and cause complete transmission failure.
The Solution:
- Use single-mode fiber for long-distance transmissions (up to 100 km).
- Use multimode fiber for shorter distances (typically under 2 km).
- Consider using repeaters or signal boosters if extending beyond recommended limits.
Planning distances carefully ensures optimal data transmission.
7. Mixing Single-Mode and Multimode Fiber
The Mistake: Single-mode and multimode fibers differ in core size and light transmission methods. Mixing them in a network can cause signal loss and performance issues due to mismatched light propagation.
The Solution: Choose the right fiber type based on network requirements. Ensure all fiber segments match in mode type, connectors, and transceivers to avoid costly compatibility issues.
8. Ignoring Proper Vertical Cable Support
The Mistake: Vertical fiber optic runs require structured support. Without proper management, the weight of the cables can create stress points, leading to fiber strand breakage or long-term performance degradation.
The Solution: Use structured cable management solutions such as:
- Fiber cable trays and ducts to prevent excessive sagging.
- Vertical support grips to distribute cable weight evenly.
- Slack storage solutions to minimize unnecessary tension.
Proper support prevents fiber damage and ensures a stable connection.
9. Overlooking End-Face Compatibility
The Mistake: Fiber optic connectors have different end-face finishes, such as PC (Physical Contact), UPC (Ultra Physical Contact), and APC (Angled Physical Contact). Using incompatible end faces can lead to reflection loss and degraded signal quality.
The Solution: Match connector end faces to ensure optimal performance. For example:
- APC connectors work best for applications that require low back-reflection, such as video and RF signals.
- UPC connectors are common in telecom applications and provide low insertion loss.
- PC connectors are standard for basic data transmissions.
Understanding end-face compatibility minimizes signal interference and ensures efficient data transfer.
Trust the Experts at Aspen Communications
Avoiding these fiber optic installation mistakes is crucial for a high-performance, long-lasting network. Whether planning a new installation or upgrading an existing system, choosing the right installation practices ensures efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Aspen Communications LLC specializes in designing, installing, and maintaining fiber optic networks for commercial and federal clients across Northern Arizona. Our certified professionals ensure that every fiber optic project is executed with precision and expertise.
Ready for a reliable fiber optic installation? Contact Aspen Communications today and ensure your network is built for the future.